 
 



|
  |
 


|
|
| |
|
General Features of the
Models

|
|
The MefLag system consists of three organically integrated mathematical finite element models, namely
MEFH, MEFD e MEFQ. This system embraces all aspects involved in simulating hydro-dispersive and ecological-environmental processes in shallow water systems like bays and lagoons.
In particular, MEFH was developed to analyze the phenomenon of tide propagation in bidimensional hydrodynamic systems; MEFD to study the diffusion and transportation of conservative substances spread by the tidal current; and MEFQ to simulate chemical-biological reactions among different constituents.
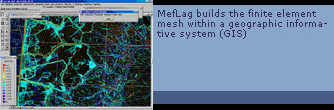
These are powerful tools, which are crucial and almost essential to understand the chemical-biological phenomena taking place in a lagoon. In order to use the models it is enough to ”draw” on the screen the finite element mesh of the physical system under review and to allocate to such elements their physical features using the Preprocessor Menu commands. Then, data are processed and results are visualized by a simple “click” through the Postprocessor.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
MefLag,
which is developed in a MicroStation environment, constitutes a real GIS system, where the mathematical models are perfectly integrated. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
Development and Analysis Tools
|
|
|
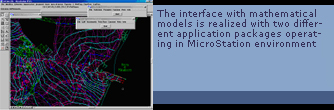
In order to set the physical features of the lagoon and to visualize the results from the models, two different application packages have been developed, operating in MicroStation environment, i.e. the preprocessor PreM2d and the postprocessor PstM2d. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
L
The tidal propagation in bays, estuaries and lagoons, when there is no great difference of density along the vertical and relevant stratification phenomena, can be mathematically represented through the resolution of the shallow water hydrodynamic equations. MEFH allows studying this important physical phenomenon using the finite element resolution technique. The particular methodology adopted in developing the MEFH model's resolution algorithms (two levels semi-implicit method), together with an accurate schematization of the hydrodynamic system by means of finite elements, allows for an accurate resolution of the continuity and momentum equations. |
|
| |
|

|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
In hydrodynamic systems like bays and lagoons, where flow primarily takes place on the horizontal plan not being present substantial stratification phenomenon, also the dispersive phenomenon shows bidimensional characteristics. MEFD is a finite element model of Eulerian-Lagrangian type that, exploiting the results of the MEFH hydrodynamic model and using the same finite element mesh, allows solving the problem of dispersion of conservative substances in 2D hydrodynamic systems. |
|
| |
|

|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
In order to appraise ecological-environmental conditions, the kinetic processes of transformation and mutual interaction of thermal energy as well as of both the biotic and the abiotic material passively transported by the moving fluid mass need to be taken into consideration. MEFQ is a finite element water quality model that, being organically integrated with the dispersive model MEFD, allows simulating the chemical-biological reactions intervening among different constituents. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
The models have been applied, inter alia, also to the particular case of the Venice lagoon, which is a very complex and delicate hydrodynamic system, where a very wide net of deep channels ploughs vast areas of low waters. |
|
| |
|

|
|


|

